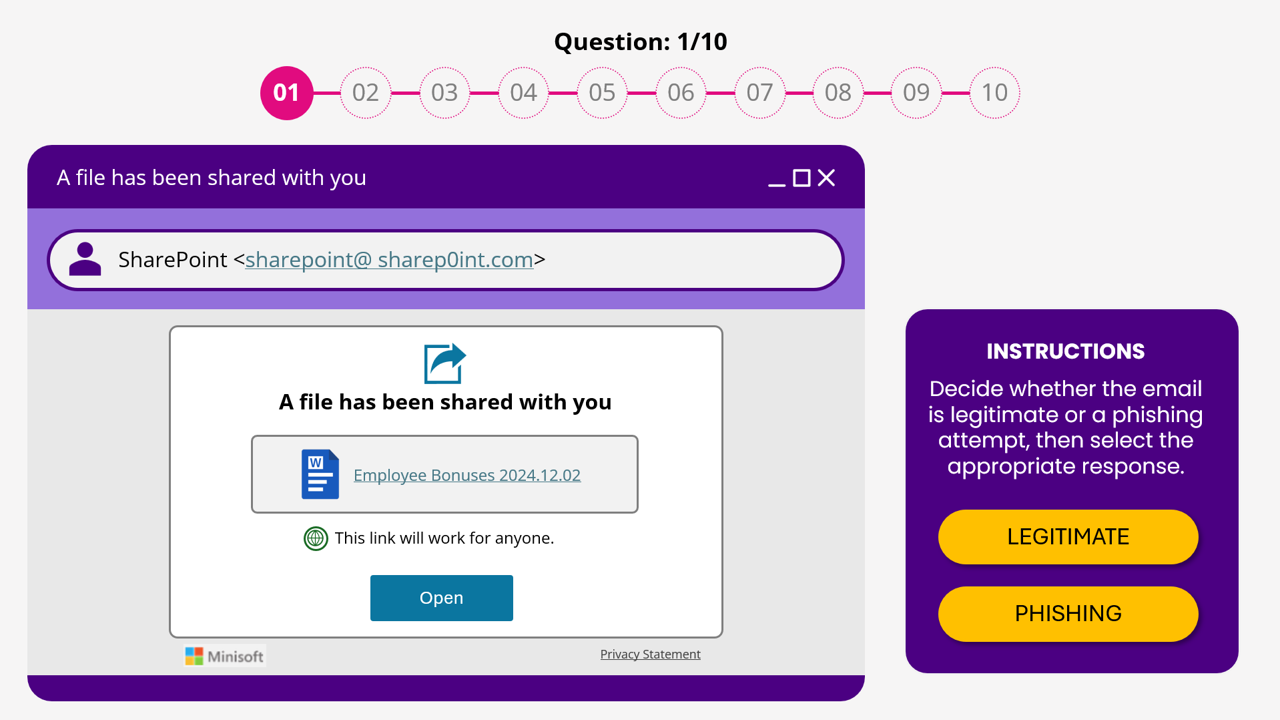
Think you can spot a Phishing Scam?
DESIGN PROPOSAL FOR
Click the buttons above to review the final product.
This design proposal outlines an interactive, scenario-based cybersecurity training program that allows employees to either refresh their knowledge or complete an adaptive phishing simulation, ensuring efficient compliance while enhancing engagement and real-world threat recognition.
Context of the Problem
Cybersecurity in Australia
Cybersecurity remains a crucial issue in Australia, significantly impacting both businesses and consumers. The country has witnessed a notable increase in cyberattacks, with reports indicating an 8% rise over the past year, particularly affecting small businesses and private schools (Feiam, 2024). Noteworthy incidents, such as the 2022 Optus data breach, have compromised the personal information of millions, leading to substantial financial losses and a decline in consumer trust (Paul, 2022). In response, the Australian government has implemented robust cybersecurity measures, including the creation of the 2023–2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy (Cybersecurity 2024, 2024), aimed at strengthening the nation’s cyber resilience. Nevertheless, the growing sophistication of cyber threats underscores the ongoing necessity for vigilance and proactive security practices among all stakeholders.
The Problem
With the rising occurrence of data breaches and the negative impact of cybersecurity incidents, the client aims to improve awareness by increasing employee vigilance in identifying phishing scams via emails and spoof websites. Data analysis indicates that the current course lacks engagement, leading to low retention rates and potential compliance concerns. The existing training primarily consists of text-based reviews of cybersecurity concepts without interactive or hands-on components to reinforce learning effectively. Without practical application or scenario-based exercises, employees struggle to recognise evolving phishing tactics in real-world situations. Enhancing the course with interactive simulations, gamified learning, and real-time threat scenarios will significantly improve knowledge retention and proactive cybersecurity behaviours, ensuring the organisation is excels at meeting their data security obligations.
Target Audience
The target audience for this cybersecurity awareness training course includes office-based employees at an accounting firm in Melbourne, Australia. This diverse group regularly handles emails, accesses company systems, and manages sensitive information, making them vulnerable to phishing attacks and social engineering scams. Human errors are responsible for over 74% of data breaches (Karl, 2024), emphasising the need for an effective training solution. Participants range from entry-level to senior employees, with most displaying basic to intermediate digital skills. Over 60% are recent graduates with limited exposure to cybersecurity threats. Given their time constraints, a concise, engaging, and interactive course format is essential. With the average cost of a data breach in Australia reaching $4.26 million in 2024 (Knowles, 2024), it is crucial that staff gain the skills to protect themselves and their organisation.
The Solution
The Final Product
Training will be delivered through an interactive, scenario-based online Microsoft PowerPoint simulation designed to enhance employees' awareness of phishing threats. Participants will have the option to either review cybersecurity fundamentals and refresh their knowledge of identifying threats or jump straight into an interactive assessment. This flexibility allows employees to efficiently meet compliance requirements while also giving those who need a refresher the opportunity to engage with key cybersecurity concepts.
The simulation will present real-world phishing scenarios, requiring users to take appropriate actions such as reporting, deleting, or flagging suspicious emails. It will dynamically adapt based on user performance, reinforcing learning through immediate feedback and branching scenarios that tailor the experience to individual knowledge levels.
Instructional Strategies - using a “Problem-Based Learning” approach
Learners engage with a realistic inbox simulation, where they analyze and respond to emails that closely resemble actual phishing attempts. This immersive, hands-on approach helps them develop practical skills for identifying and managing security threats. Studies have shown that interactive, scenario-based training methods significantly improve employees' ability to recognise and respond appropriately to phishing attempts (Prummer et al., 2024). For example, research indicates that involving employees in real-world attack simulations enhances their retention and application of security practices (Prummer et al., 2024).
Additionally, offering flexible training options that cater to various learning preferences and schedules can boost employee engagement and satisfaction (Reynolds, 2023), leading to better compliance with cybersecurity protocols.
Engagement Strategies - using “Gamification Elements”
Gamification in eLearning enhances engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention by incorporating interactive elements like challenges, rewards, and real-world scenarios, making learning more immersive and effective (Pappas, 2024).
Interactive Decision Points
Learners click on emails, hover over links, and inspect attachments to make informed decisions.Instant Feedback & Reinforcement
Immediate responses explain why an email is safe or malicious, reinforcing key concepts.Scoring System & Completion Confirmation
Employees must achieve a minimum passing score, ensuring compliance with company policies.
Assessment Strategies - using “Scenario-Based Simulations”
The assessment strategy for this cybersecurity training program focuses on interactive, scenario-based simulations that provide immediate feedback to participants. Employees engage with realistic phishing scenarios, making decisions such as reporting, deleting, or flagging suspicious emails. They receive instant responses that reinforce correct actions and correct any misconceptions. This immediate feedback mechanism is crucial, as it allows learners to quickly identify and address errors, enhancing knowledge retention and promoting the development of metacognitive skills. Research shows that timely feedback not only corrects misunderstandings but also increases learner engagement and motivation (Yu & Cai, 2022). By incorporating these elements, the training ensures that employees can effectively recognize and respond to cybersecurity threats, thereby strengthening the organization’s overall security posture.
Design Considerations
No Subscriptions or Software Purchases
The client requires an LMS-free, software-independent solution that continues to provide an engaging eLearning-style experience but does not wish to invest in learning management systems or online eLearning authoring software as it does not see a return on investment for a single course. Without access to eLearning authoring tools or an LMS, traditional interactive course development using digital affordances is not an option.
The challenge is to design a dynamic, gamified simulation using Microsoft PowerPoint—ensuring it remained interactive, visually engaging, and assessment-driven. Additionally, the solution had to offer real-time feedback and trackable completion status to meet compliance requirements—all without relying on standard digital learning tools. The final design requires a balance of interactivity, engagement, and scalability while remaining accessible to all employees.
Practice
Incorporating practical exercises into training courses that help employees identify phishing threats is essential for enhancing cybersecurity awareness and resilience. Simulated phishing campaigns, in which organisations send or mimic deceptive emails to their own staff to evaluate their responses, are an effective way to assess and improve employees' ability to recognise and respond appropriately to phishing attempts (Prummer et al., 2024).
These simulations provide a direct measure of staff compliance and, when conducted regularly, can track improvements in user behaviour. This approach reinforces learning by offering immediate feedback and real-world application. And with the average cost of a data breach in Australia reaching over $4 million (Knowles, 2024), it is vitally important for organisations to ensure their staff are trained to identify and respond to each threat appropriately.
Accessibility
The cybersecurity training course is designed to be fully accessible for users both in the office and remotely, ensuring flexibility and convenience for all employees. Hosted on a cloud-based server, the course can be accessed from various devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, allowing employees to complete training at their own pace, regardless of location. This accessibility is critical in today’s hybrid and remote work environments, where employees may not always be in a traditional office setting but still need to stay vigilant against cybersecurity threats. By ensuring compatibility across multiple devices and offering an intuitive, responsive design, the course removes barriers to participation, making it easier for employees to engage with training materials and meet compliance requirements. Additionally, this approach ensures that remote workers, who may be at a higher risk of phishing attacks due to decentralised security protections, receive the same level of training and preparedness as their in-office counterparts.
Engagement
Engagement is a critical factor in learning design, as it directly influences knowledge retention, participation, and the overall effectiveness of training programs. The client’s previous cybersecurity course struggled with engagement, leading to low retention rates and potential compliance risks due to its heavy reliance on text-based content without interactive elements.
Research shows that interactive and scenario-based learning improves learner motivation and real-world application of skills, making training more impactful (Arunkumar, 2025). By integrating gamification, real-time feedback, and practical exercises, this new course ensures that employees remain engaged, increasing their ability to recognise and respond to cybersecurity threats effectively.
References
Arunkumar, P. (2025). Scenario-Based Learning: Enhancing Education Through Real-World Context. eLearningDOC. https://elearningdoc.com/scenario-based-learning/
Cybersecurity 2024. (2024, March 14). Chambers and Partners. https://practiceguides.chambers.com/practice-guides/cybersecurity-2024/australia/trends-and-developments
Feiam, A. (2024, November 20). Cyber criminals ramping up attacks against private schools. news.com.au. https://www.news.com.au/technology/online/security/cyber-criminals-ramping-up-attacks-against-private-schools/news-story/91c2081e527cb38b8d75e843e4277ef2
Karl, T. (2024, April 19). Understanding the Importance of Cybersecurity Awareness Training. New Horizons. https://www.newhorizons.com/resources/blog/the-importance-of-cybersecurity-awareness-training
Knowles, C. (2024, August 2). Average cost of an Australian data breach hits AUD $4.26 million. SecurityBrief Australia. https://securitybrief.com.au/story/average-cost-of-an-australian-data-breach-hits-aud-4-26-million
Pappas, C. (2024, December 3). The Science And Benefits Of Gamification In eLearning. eLearning Industry. https://elearningindustry.com/science-benefits-gamification-elearning
Paul, S. (2022, December 21). Inside the Optus hack that woke up Australia. Australian Financial Review. https://www.afr.com/technology/inside-the-optus-hack-that-woke-up-australia-20221123-p5c0lm
Prummer, J., Van Steen, T., & Van Den Berg, B. (2024, January). A systematic review of current cybersecurity training methods. Computers & Security. Volume 136, Article 103585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2023.103585
Reynolds, K. (2023, May 25). The Value of Flexible Training Options. Training. https://trainingmag.com/the-value-of-flexible-training-options/
Yu, R., & Cai, X. (2022, June 30). Imact of Immediacy of Feedback on Continuous Intentions to Use Online Learning From the Student Perspective. Frontiers in Psychology. Volume 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.865680